What is this article about?
Companies must remain innovative and disrupt themselves from within! The competition for outside the box and creative minds is increasing! Innovation management is a must, otherwise you won't be able to keep up with the fast-paced competition!
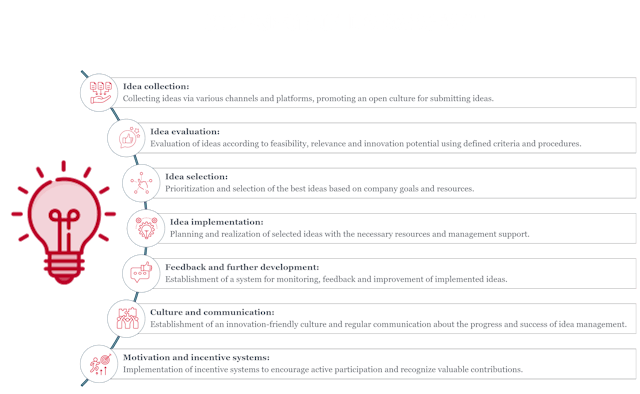
You've probably heard one or two of these things before. But is the topic of innovation management being tackled properly? What are the steps that need to be taken at the beginning?
In this blog post, we would like to take a closer look at the various approaches to innovation management and provide you with two creativity techniques that can be helpful when developing new ideas, concepts or even innovation processes.